CURRENT AFFAIRS
Get the most updated and recent current affair content on Padhaikaro.com
Blue straggler - bigger and bluer star formation
- Integrity Education, Delhi
- 03, Sep 2021
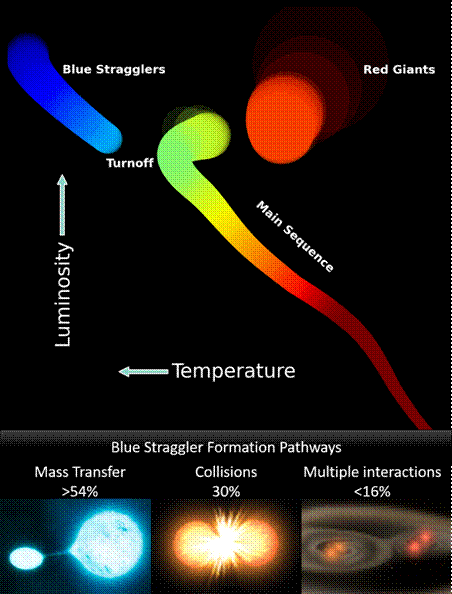
- A blue straggler is a main-sequence star in an open or globular cluster that is more luminous and bluer than stars at the main sequence turnoff point for the cluster.
- Blue stragglers were first discovered by Allan Sandage in 1953
- Indian researchers found that half of the blue stragglers in their sample are formed through mass transfer from a close binary companion star, one third are likely formed through collisions of 2 stars, and the remaining are formed through interactions of more than 2 stars.
Formation Process
- A bunch of stars born at the same time from the same cloud form a star cluster.
- As time passes, each star evolves differently depending on its mass.
- The most massive and bright stars evolve and move off the main sequence creating a bend in their track, known as the turnoff.
- Some stars seem to be hotter than the turnoff of the parent cluster, they are termed “Blue Stragglers”