CURRENT AFFAIRS
Get the most updated and recent current affair content on Padhaikaro.com
Daily Current Affairs - 21-08-2021
- IAS NEXT, Lucknow
- 21, Aug 2021

Reference News
- The Social Justice Ministry issued a notification saying that Section 34 of the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 , which provides for 4% reservation in jobs for PwD in government establishments, would not apply to all categories of posts of IPS, the Indian Railway Protection Force Service and the police forces of Delhi, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep and Daman and Diu and Dadra and Nagar Haveli.
- At the same time, the Ministry issued another notification making a distinction between combat and non-combat roles in the security forces.
- The Ministry exempted all combat posts in the Border Security Force, the Central Reserve Police Force, the Central Industrial Security Force, the Indo-Tibetan Border Police, the Sashastra Seema Bal and the Assam Rifles from the non-discrimination and reservation provisions of the RPD Act.
Concerns:
- The provisions of the Act did not intend to give blanket exemptions from hiring PwD, but to make sure that combat roles are not assigned to them.
- There are many roles that PwD could fill within police forces and exempting all categories of roles is wrong, as per rights groups.
Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016
- It replaced the 1995 Act.
- It brought Indian law in line with the United National Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD), to which India is a signatory.
- Disability has been defined based on an evolving and dynamic concept.
- The types of disabilities have been increased from existing 7 to 21 and the Central Government will have the power to add more types of disabilities.
- Speech and Language Disability and Specific Learning Disability have been added for the first time.
- Acid Attack Victims have been included.
- In addition, the Government has been authorized to notify any other category of specified disability.
- The appropriate governments have been given the responsibility to take effective measures to ensure that the persons with disabilities enjoy their rights equally with others.
- Every child with benchmark disability between the age group of 6 and 18 years shall have the right to free education.
- Government funded educational institutions as well as the government recognized institutions will have to provide inclusive education to the children with disabilities.
- It provides for penalties for offences committed against persons with disabilities and also violation of the provisions of the new law.
Register of Indigenous Inhabitants of Nagaland (RIIN)
Reference news-
Nagaland Chief Minister has sought to reduce fears over an exercise similar to Assam’s National
Register of Citizens.
Next Analysis-
What is Register of Indigenous Inhabitants of Nagaland?
- The RIIN will be the master list of all indigenous inhabitants of the state.
- Objective: To prevent outsiders from obtaining fake indigenous certificates for seeking jobs and benefits of government schemes.
- The RIIN will be prepared after an extensive survey with the help of a village-wise and wardwise list of indigenous inhabitants based on official records.
- It will be prepared under the supervision of each district administration.
- No fresh indigenous inhabitant certificate will be issued after the RIIN is completed except for children born to the State’s indigenous inhabitants who will be issued indigenous certificates along with birth certificates. The RIIN database will be updated accordingly.
- The RIIN will also be integrated with the online system for Inner-Line Permit, a temporary document non-inhabitants are required to possess for entry into and travel in Nagaland.
- The entire exercise will be monitored by the Commissioner of Nagaland. In addition, the state government will designate nodal officers of the rank of a Secretary to the state government.
Progress
- The State government, through a notification on June 29, 2019, had decided to update the Register of Indigenous Inhabitants of Nagaland (RIIN) with December 1, 1963 ((the day Nagaland attained statehood), as the cut-off date for the inclusion of people in it.
- The exercise was put on hold after opposition from various quarters, which demanded that the cut-off date be changed to April 28, 1977, when the government laid down the criteria for issuing indigenous inhabitant certificates to the residents.
Concerns
- Exclusion: The exercise is feared to leave out certain Nagas and non-Nagas for their eventual eviction or denial of opportunities.
- The non-indigenous Nagas could be treated as “illegal immigrants”
- Loss of Property
Japan aims to bring back soil samples from Mars moon by 2029
Reference news:
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, or JAXA, plans to launch an explorer in 2024 to land on Phobos, a Martian moon, to collect 10 grams of soil and bring it back to Earth in 2029 (ahead of the United States and China)
Next Analysis-
Key details
- Soil on Phobos is likely to be a mixture of material from the moon itself and material from Mars that was spread by sandstorms.
- Significance: Collecting samples from multiple locations on Phobos could provide a greater chance of obtaining possible traces of life from Mars.
- Scientists also hope to learn about the evolution of the Martian biosphere.
Do you know?
- NASA’s Perseverance rover has landed in a Mars crater where it is to collect 31 samples that are to be returned to Earth with help from the European Space Agency as early as 2031.
- China in May became the second country to land and operate a spacecraft on Mars and plans to bring back samples around 2030.
Earlier missions
- Two other NASA landers are also operating on Mars — 2018’s InSight and 2012’s Curiosity rover.
- Currently, following mission are exploring Mars:
- Three from the U.S. – Odyssey, MAVEN, Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, Mars 2020 (Perseverance Rover & Ingenuity Helicopter)
- Two from Europe – Exo Mars, Mars Express
- One from India – Mangalyaan
- One from China – Tianwen-1 (orbiter & rover)
- One from UAE – Emirates Mars Mission, Hope Spacecraft
UNITE Aware
Reference news-
External Affairs Minister has announced the rollout of a situational awareness platform in partnership with the UN — ‘UNITE Aware’ — to help enhance the safety of UN peacekeepers.
- This was announced during the recent United Nations Security Council (UNSC) open debate on technology and peacekeeping.
What is UNITE AWARE?
- UNITE AWARE is a mobile tech platform developed by India to provide terrain-related information to the UN peacekeepers so as to ensure their safety.
- It is being developed in partnership with the UN Department of Peacekeeping Operations and the Department of Operational Support.
- India has spent 1.64 million USD for this project.
- This initiative is based on the expectation that an entire peacekeeping operation can be visualized, coordinated, and monitored on a real-time basis.
- What is peacekeeping?
- The United Nations Peacekeeping operations are policing and peacebuilding actions carried out by the UN to bring order and stability in wartorn nations.
- Every peacekeeping mission is authorized by the Security Council.
Composition:
- Peacekeeping forces are contributed by member states on a voluntary basis.
- UN peacekeepers (often referred to as Blue Berets or Blue Helmets because of their light blue berets or helmets) can include soldiers, police officers, and civilian personnel.
- Civilian staff of peace operations are international civil servants, recruited and deployed by the UN Secretariat.
- UN Peacekeeping is guided by three basic principles:
- Consent of the parties.
- Impartiality.
- Non-use of force except in self-defence and defence of the mandate.
Do you know?
- The top 5 providers of assessed contributions to United Nations Peacekeeping operations for 2020-2021 are:
- United States (27.89%).
- China (15.21%).
- Japan (8.56%).
- Germany (6.09%).
- United Kingdom (5.79%).
New Species of Cascade Frog: Arunachal Pradesh
Reference News-
Recently, a team of researchers have discovered a new species of cascade frog in Arunachal Pradesh named Adi Cascade Frog.
- Earlier, a new frog species named Minervarya Pentali was discovered in the Western Ghats.
About:
- It is a predominantly brown colour frog, with a size ranging roughly between 4 cm to 7 cm. It is formally described as Amolops adicolasp.nov., which is morphologically distinguished from its congeners by a suite of characters that include adult size, body colouration and markings, skin texture, snout shape, foot webbing and digit tip morphology.
- It has been named Adi Cascade Frog (Amolops Adicola) after the indigenous Adi tribe living in the Adi hills of Arunachal Pradesh. The literal meaning of Adi is “hill” or “mountain top. Historically, this region was also known as Abor hills (Arunachal Pradesh).
- Cascade frogs are named so because of their preference of small waterfalls or cascades in flowing hill streams.
Cascade Frogs belong to the genus Amolops-
- The genus Amolops is one of the largest groups of ranid frogs (family Ranidae) with currently 73 known species that are widely distributed across Northeast and North India, Nepal, Bhutan, China, through Indochina, to the Malay Peninsula.
DAILY TOPIC
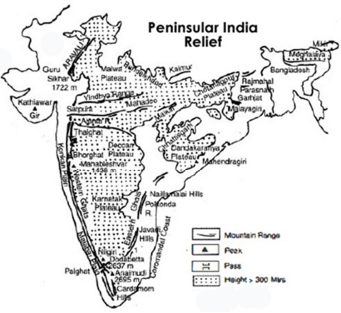
The Peninsular India comprises the diverse topological and climatic patterns of South India. The Peninsula is in shape of a vast inverted triangle, bounded on the west by the Arabian Sea, on the east by the Bay of Bengal and on the north by the Vindhya and Satpura ranges. The line created by the Narmada river and Mahanadi river is the traditional boundary between northern and southern India. Covering an area of about 16 Lakh km², the peninsular upland forms the largest physiographic division of India. It is bounded by the Aravallis in the North West, Hazaribagh and Rajmahal Hills in the northeast, the Western Ghats (Sahayadri Mountains) in the west and the Eastern Ghats in the east. The highest peak of Peninsular India is Anamudi that is 2695 metres above sea level.
The narrow strip of verdant land between the Western Ghats and the Arabian Sea is the Konkan region; the term encompasses the area south of the Narmada as far as Goa. The Western Ghats continue south, forming the Malnad (Canara) region along the Karnataka coast, and terminate at the Nilgiri mountains, an inward (easterly) extension of the Western Ghats. The Nilgiris run in a crescent approximately along the borders of Tamil Nadu with northern Kerala and Karnataka, encompassing the Palakkad and Wayanad hills, and the Satyamangalam ranges, and extending on to the relatively low-lying hills of the Eastern Ghats, on the western portion of the Tamil Nadu–Andhra Pradesh border. The Tirupati and Anaimalai hills form part of this range.
The Deccan plateau, covering the major portion of the states of Maharashtra, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, is the vast elevated region bound by the C-shape defined by all these mountain ranges. No major elevations border the plateau to the east, and it slopes gently from the Western Ghats to the eastern coast.
The Peninsular India can be divided into four regions viz. Central Highlands, Deccan Plateau, Western Ghats or Sahayadri and Eastern Ghats.