CURRENT AFFAIRS
Get the most updated and recent current affair content on Padhaikaro.com
Authoritarianism is on the rise, says report
- IAS NEXT, Lucknow
- 24, Nov 2021
The Global State of Democracy Report, 2021 was recently released by the International Institute for Democracy and Electoral Assistance.
- The reports refer to three main regime types: democracies, hybrid and authoritarian regimes. Hybrid and authoritarian regimes are both classified as non-democratic.
Highlights of the Report:
- The number of countries moving towards authorianism in 2020 was higher than that of
countries going in the other direction, towards democracy. 20 countries moved in the direction of authoritarianism, seven countries moved towards democracy.
- The pandemic has prolonged this existing negative trend into a five-year stretch, the longest such period since the start of the third wave of democratisation in the 1970s.
- Democratically elected Governments, including established democracies, are increasingly adopting authoritarian tactics.
Performance analysis of various studies:
- The report highlighted the case of Brazil and India as “some of the most worrying examples of backsliding”. However, India remained in the category of a mid-level performing democracy as it has since 2000.
- The United States and three members of the European Union [Hungary, Poland and Slovenia] have also seen concerning democratic declines.

About the Report:
- The Global State of Democracy 2021 reviews the state of democracy around the world over the course of 2020 and 2021, with democratic trends since 2015 used as contextual reference.
- It is based on analysis of events that have impacted democratic governance globally since the start of the pandemic, based on various data sources, including International IDEA’s Global Monitor of Covid-19’s Impact on Democracy and Human Rights, and International IDEA’s Global State of Democracy (GSoD) Indices.
- The GSoD Indices provide quantitative data on democratic quality for the same countries, based on 28 aspects of democracy up until the end of 2020.
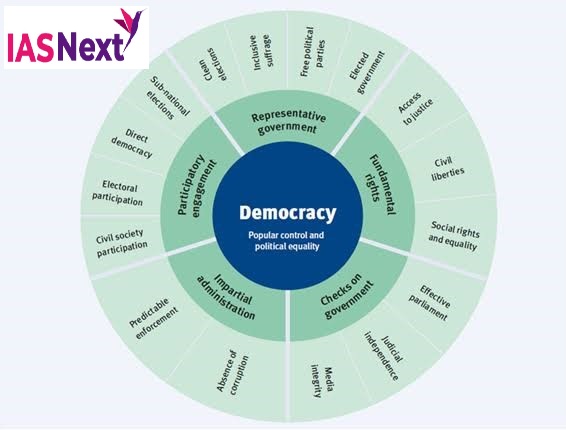
What is democracy?
The report defines democracy as based on five core attributes: Representative Government, Fundamental Rights, Checks on Government, Impartial Administration and Participatory Engagement. These five attributes provide the organizing structure for this report.