CURRENT AFFAIRS
Get the most updated and recent current affair content on Padhaikaro.com
Kunming Declaration on biodiversity conservation
- IAS NEXT, Lucknow
- 20, Oct 2021

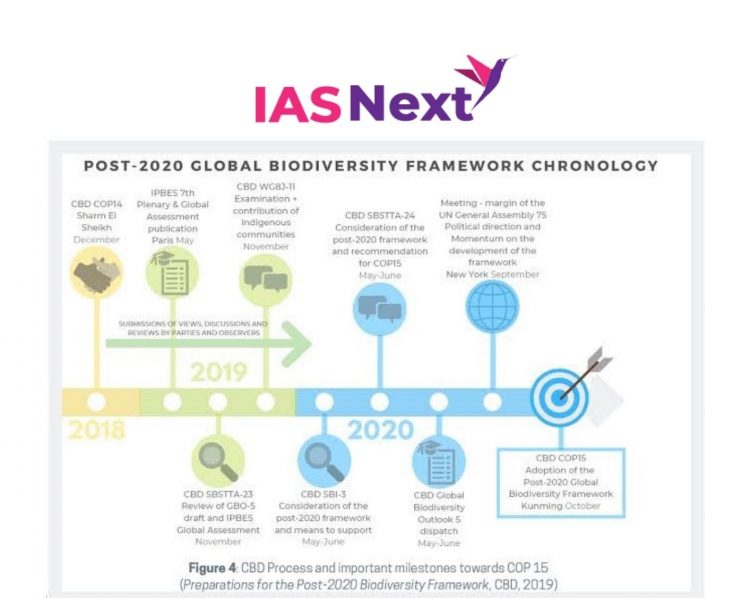
The “Kunming Declaration” was adopted by over 100 countries in the ongoing virtual 15th meeting of the Conference of the Parties (COP) to the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity (UNCBD).
Theme of the COP-15: “Ecological Civilization: Building a Shared Future for All Life on Earth”.
Kunming Declaration:
- It calls upon the parties to “mainstream” biodiversity protection in decision-making and recognise the importance of conservation in protecting human health.
- By adopting this, the nations have committed themselves to support the development, adoption and implementation of an effective post-2020 implementation plan, capacity building action plan for the Cartagena Protocol on biosafety.
- Signatory nations should ensure that the post-pandemic recovery plans contribute to the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity, promoting sustainable and inclusive development.
- The declaration expects signatory nations to synchronize Biodiversity plans with the three UN decades program which are on ‘Sustainable Development’, ‘Ecosystem Restoration’, ‘Ocean Science for Sustainable Development’.
Convention on Biological Diversity, 1992:
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) entered into force on 29 December 1993. It has 3 main objectives:
- The conservation of biological diversity.
- The sustainable use of the components of biological diversity.
- The fair and equitable sharing of the benefits arising out of the utilization of genetic resources.
The Convention was opened for signature on 5 June 1992 at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (the Rio “Earth Summit”).
- This convention is a legally binding framework treaty that has been ratified by180 countries.
- The CBD Secretariat is based in Montreal, Canada and it operates under the United Nations Environment Programme.
- The areas that are dealt by convention are conservation of biodiversity,sustainable use of biological resources and equitable sharing of benefits arising from their sustainable use.
- The convention came into force in 1993. Many biodiversity issues are addressed including habitat preservation, intellectual property rights, biosafety andindigenous people‘s rights.
30 by 30 Target:
The declaration made a reference to the ’30 by 30′ target which is a key proposal being debated at the COP15, that would afford 30% of the Earth’s land and oceans protected status by 2030.
- Apart from this, the goal to halve the use of chemicals in agriculture and stop creating plastic waste is also being debated.