CURRENT AFFAIRS
Get the most updated and recent current affair content on Padhaikaro.com
Leaded Petrol
- Vaid's ICS, Lucknow
- 01, Sep 2021

Why in News:
The use of leaded petrol has been eradicated from the globe as per the observation made by UNEP
- Achieving of this milestone will prevent more than 1.2 million premature deaths and save world economies over $2.4 trillion annually
- Algeria — the last country to use the fuel — exhausted its supplies last month
- India banned leaded petrol in March 2000
Harmful effects of leaded petrol:
- Lead exposure can have serious consequences for the health of children. At high levels of exposure, lead attacks the brain and central nervous system to cause coma, convulsions and even death. Children who survive severe lead poisoning may be left with mental retardation and behavioral disorders.
- Lead in bone is released into blood during pregnancy and becomes a source of exposure to the developing fetus.
- The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) estimated that in 2017, lead exposure accounted for 1.06 million deaths and 24.4 million years of healthy life lost (disability-adjusted life years (DALYs)) worldwide due to long-term effects on health.
- Lead also causes long-term harm in adults, including increased risk of high blood pressure and kidney damage.
About UNEP
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is the leading global environmental authority that sets the global environmental agenda, promotes the coherent implementation of the environmental dimension of sustainable development within the United Nations system, and serves as an authoritative advocate for the global environment.
It aims to provide leadership and encourage partnership in caring for the environment by inspiring, informing, and enabling nations and peoples to improve their quality of life without compromising that of future generations.
It is headquartered in Nairobi, Kenya:
- The broad areas where UNEP focuses are: climate change, disasters and conflicts, ecosystem management, environmental governance, chemicals and waste, resource efficiency, and environment under review
- The UNEP is funded by voluntary contributions of its members
- It hosts the secretariats of many critical multilateral environmental agreements and research bodies, bringing together nations and the environmental community to tackle the greatest challenges of our time.
These include the following:
- The Convention on Biological Diversity
- The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora
- The Minamata Convention on Mercury
- The Basel, Rotterdam and Stockholm Conventions
- The Vienna Convention for the Protection of Ozone Layer and the Montreal Protocol
- The Convention on Migratory Species
- The Carpathian Convention
- The Bamako Convention
- The Tehran Convention

Facts for Prelims:
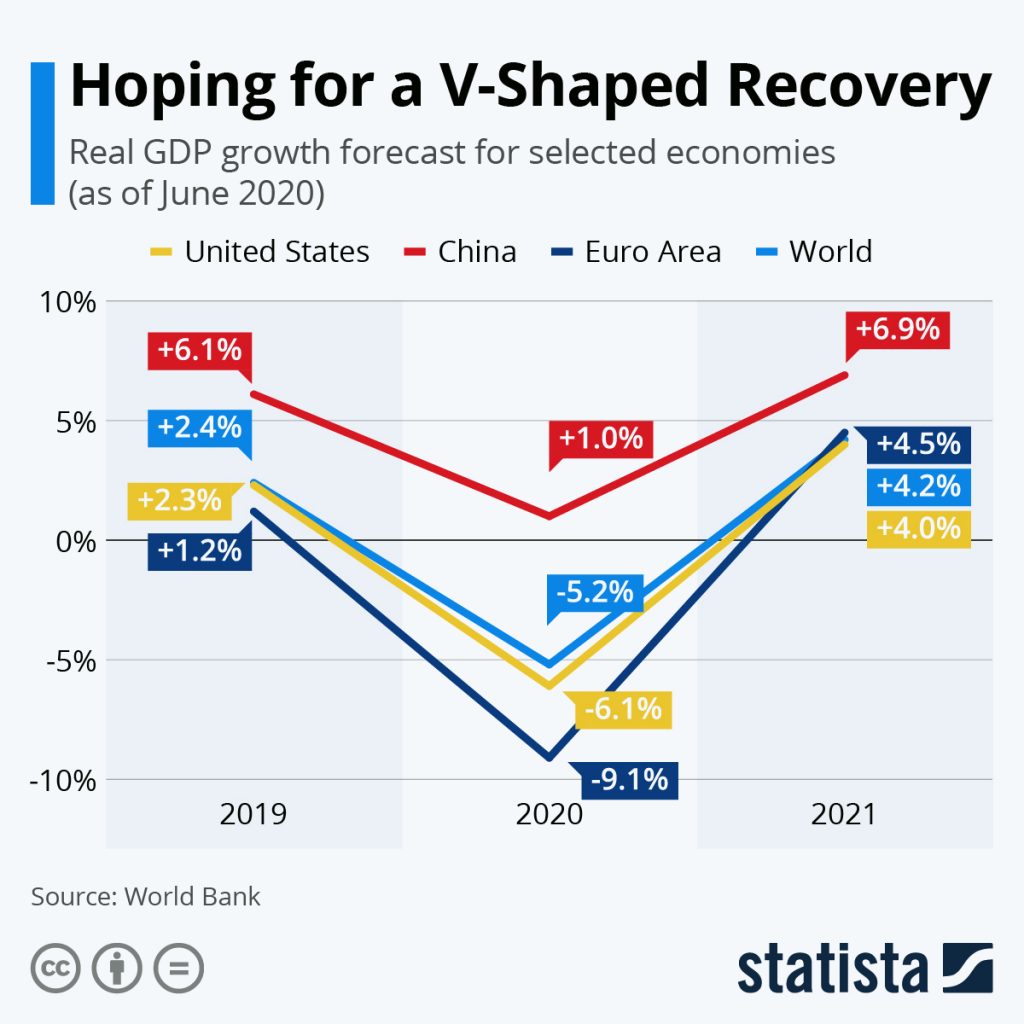
Shaped recovery
V-shaped recovery is a type of economic recession and recovery that resembles a “V” shape in charting. Specifically, a V-shaped recovery represents the shape of a chart of economic measures economists create when examining recessions and recoveries.
The Bamako Convention
- The Bamako Convention is a treaty of African nations prohibiting the import of any hazardous waste.
- The Convention was negotiated by twelve nations of the Organisation of African Unity at Bamako, Mali in January, 1991, and came into force in 1998.