CURRENT AFFAIRS
Get the most updated and recent current affair content on Padhaikaro.com
New Crypto Bill
- IAS NEXT, Lucknow
- 25, Nov 2021

Reference News:
The Cryptocurrency and Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill, 2021 will introduce in the winter session of Parliament.
Key Provisions:
- It seeks to regulate cryptocurrency and ostensibly ban all private cryptocurrencies.
- It seeks to create a facilitative framework for creation of the official digital currency to be issued by the Reserve Bank of India.
So far, the precise contours of the Bill are not in the public domain and no public consultations have been held.
Present status:
- An inter-ministerial panel on cryptocurrency has recommended that all private cryptocurrencies, except any virtual currencies issued by state, will be prohibited in India.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has also raised concerns on the cryptocurrencies traded in the market and conveyed them to the Centre.
- Back in March 2020, the Supreme Court had allowed banks and financial institutions to reinstate services related to cryptocurrencies by setting aside the RBI’s 2018 circular that had prohibited them (Based on the ground of “proportionality”).
What are Cryptocurrencies?
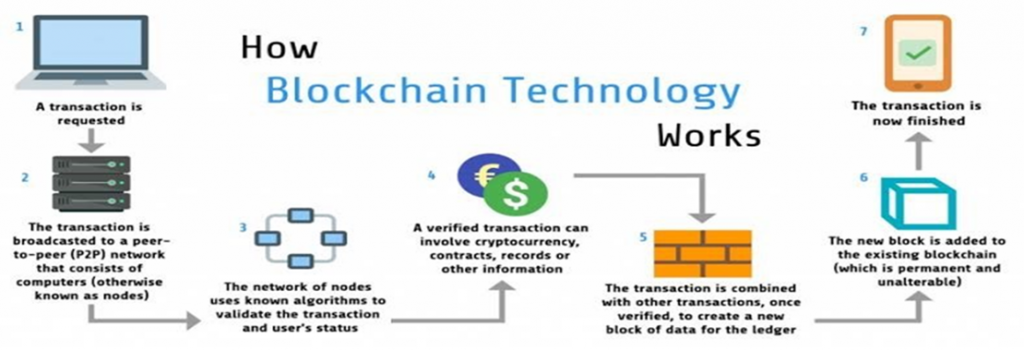
Cryptocurrencies are digital currencies in which encryption techniques are used to regulate the generation of units of currency and verify the transfer of funds, operating independently of a central bank.
Examples: Bitcoin, Ethereum etc.
Why the govt wants to ban cryptocurrencies?
- Sovereign guarantee: Cryptocurrencies pose risks to consumers. They do not have any sovereign guarantee and hence are not legal tender.
- Market volatility: Their speculative nature also makes them highly volatile. For instance, the value of Bitcoin fell from USD 20,000 in December 2017 to USD 3,800 in November 2018.
- Risk in security: A user loses access to their cryptocurrency if they lose their private key (unlike traditional digital banking accounts, this password cannot be reset).
- Malware threats: In some cases, these private keys are stored by technical service providers (cryptocurrency exchanges or wallets), which are prone to malware or hacking.
- Money laundering.