CURRENT AFFAIRS
Get the most updated and recent current affair content on Padhaikaro.com
Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) and India
- Vaid's ICS, Lucknow
- 13, Jan 2022
Why in News?
South Korea has said that it regrets India’s absence from the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) and hopes to see New Delhi rejoin the agreement.
When did it come into force?
The RCEP came into effect on January 1, 2022, marking the formation of the world’s largest free trade zone in terms of trade volume.
Why did India not join?
India withdrew from the RCEP in 2019 largely because of concerns it would open it up to Chinese goods amid an already wide trade imbalance with China, and the failure of the agreement to adequately open up to services.
Need for India’s presence in RCEP:
- India had “a crucial role” to play in helping the region build an inclusive architecture at a time of increasing global instability.
- Such trade pacts will also give Indian companies a platform to showcase their strengths across even larger markets.
- Besides, Rising U.S.-China tensions were “deeply worrying” for the region with the pandemic resulting in “heightened tension”.
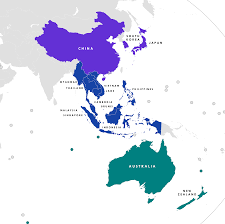
What is RCEP?
It is a trade deal between the 10-member Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and China, Japan, South Korea, Australia and New Zealand.
Aims and Objectives of RCEP:
- To lower tariffs, open up trade in services and promote investment to help emerging economies catch up with the rest of the world.
- To help reduce costs and time for companies by allowing them to export a product anywhere within the bloc without meeting separate requirements for each country.
- It also touches on intellectual property, but will not cover environmental protections and labour rights.
Significance:
- RCEP will cover about 30% of global gross domestic product (GDP), worth $26.2 trillion (€23.17 trillion), and nearly a third of the world’s population, some 2.2 billion people.
- Under RCEP, around 90% of trade tariffs within the bloc will eventually be eliminated.
- RCEP will also set common rules around trade, intellectual property, e-commerce and competition.
HINDI
UNESCO’s World Heritage Centre has agreed to publish Hindi descriptions of India’s UNESCO World Heritage Sites on its website.
The permanent delegation of India to UNESCO yesterday announced that on the occassion of World Hindi Day, UNESCO’s World Heritage Centre has agreed to publish Hindi descriptions of India’s UNESCO World Heritage Sites on WHC (Vishwa Dharohar Samiti) website