CURRENT AFFAIRS
Get the most updated and recent current affair content on Padhaikaro.com
SC, HCs can’t interfere in daily temple rituals
- IAS NEXT, Lucknow
- 18, Nov 2021

Reference News:
A writ petition was filed in the Supreme Court alleging that rituals were not being performed as per traditions at the famous Tirumala Tirupati temple.
Supreme Court’s observations:
- Constitutional courts could not interfere with day-to-day rituals and sevas performed in temples on the basis of “public interest” petitions.
- Religious scholars and priests were best equipped to go into the question whether rituals in a temple were being conducted in accordance with customs and traditions.
- In such matters, the writ jurisdiction of a constitutional court under Articles 226 and 32 was limited.
What is Article 32?
Article 32 deals with the ‘Right to Constitutional Remedies’, or affirms the right to move the Supreme Court by appropriate proceedings for the enforcement of the rights conferred in Part III of the Constitution.
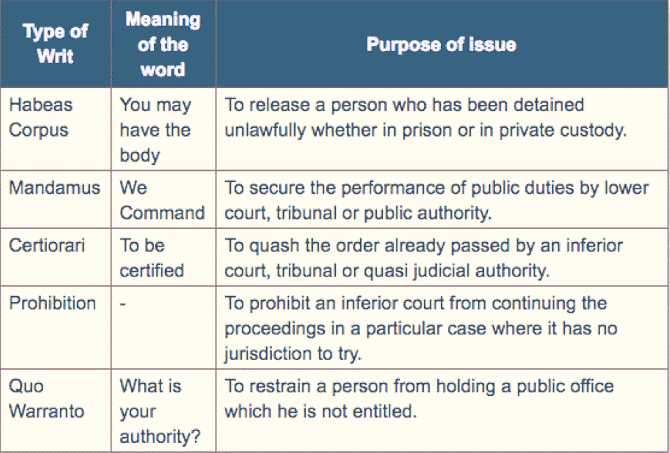
- It states that the Supreme Court “shall have power to issue directions or orders or writs, including writs in the nature of habeas corpus, mandamus, prohibition, quo warranto and certiorari, whichever may be appropriate, for the enforcement of any of the rights conferred by this Part”.
Key Points:
- The right guaranteed by this Article “shall not be suspended except as otherwise provided for by this Constitution”.
- Only if any of these fundamental rights is violated can a person can approach the Supreme Court directly under Article 32.
Can High Courts be approached in cases of violation of fundamental rights?
In civil or criminal matters, the first remedy available to an aggrieved person is that of trial courts, followed by an appeal in the High Court and then the Supreme Court.
When it comes to violation of fundamental rights, an individual can approach the High Court under Article 226 or the Supreme Court directly under Article 32.
- Article 226, however, is not a fundamental right like Article 32.
What have been the Supreme Court’s recent observations on Article 32?
In Romesh Thappar vs State of Madras (1950), the Supreme Court observed that Article 32 provides a “guaranteed” remedy for the enforcement of fundamental rights.
- This Court is thus constituted the protector and guarantor of fundamental rights, and it cannot, consistently with the responsibility so laid upon it, refuse to entertain applications seeking protection against infringements of such rights,” the court observed.
During the Emergency, in Additional District Magistrate, Jabalpur vs S S Shukla (1976), the Supreme Court had said that the citizen loses his right to approach the court under Article 32.
Finally, Constitutional experts say that it is eventually at the discretion of the Supreme Court and each individual judge to decide whether an intervention is warranted in a case, which could also be heard by the High Court first.