CURRENT AFFAIRS
Get the most updated and recent current affair content on Padhaikaro.com
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO)
- IAS NEXT, Lucknow
- 27, Nov 2021

Reference News:
At the recently held 20th meeting of the SCO Council of Heads of Government, India observed that raising bilateral issues is counterproductive to the spirit of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO).
What’s the issue?
China and Pakistan have deliberately tried to bring bilateral issues into SCO. This violates the well-established principles and norms of the SCO Charter. Such acts are counterproductive to the spirit of consensus and cooperation that define this organisation and should be condemned.
About the SCO:
The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is a permanent intergovernmental international organization.
- The creation of SCO was announced on 15 June 2001 in Shanghai (China).
- The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation Charter was signed during the St.Petersburg SCO Heads of State meeting in June 2002, and entered into force on 19 September 2003.
- It was preceded by the Shanghai Five mechanism.
- The SCO’s official languages are Russian and Chinese.
- The SCO Charter, sealed in 2002, calls for “peaceful settlement” of conflicts and disputes among member states.
Founding members of SCO were-
- The Republic of Kazakhstan,
- The People’s Republic of China,
- The Kyrgyz Republic,
- The Russian Federation,
- The Republic of Tajikistan,
- The Republic of Uzbekistan.
Background:
- Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia and Tajikistan were members of the Shanghai five, Prior to the creation of SCO in 2001.
- Shanghai Five (1996) emerged from a series of border demarcation and demilitarization talks which the four former Soviet republics held with China to ensure stability along the borders.
- Uzbekistan joined the organisation in 2001, following this the Shanghai Five was renamed the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO).
- India and Pakistan became members in 2017.
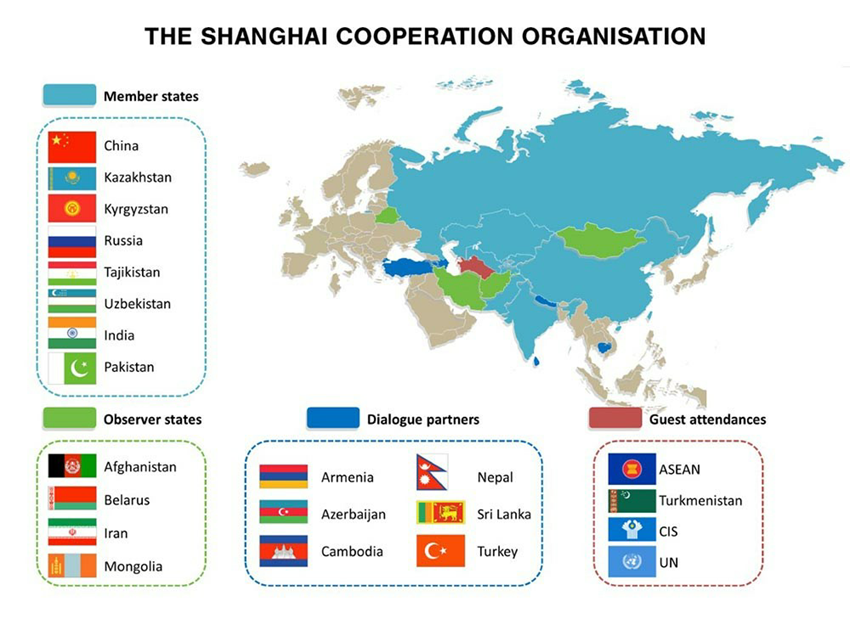
Member Countries:
Now, SCO is comprised of Eight Member countries. Namely-
- Kazakhstan
- China
- Kyrgyzstan
- Russia
- Tajikistan
- Uzbekistan
- India
- Pakistan
Objectives of SCO:
- Strengthening mutual trust and neighbourliness among the member states.
- Promoting their effective cooperation in politics, trade, the economy, research, technology and culture, as well as in education, energy, transport, tourism, environmental protection, and other areas.
- Making joint efforts to maintain and ensure peace, security and stability in the region.
- Moving towards the establishment of a democratic, fair and rational new international political and economic order.
Significance for India:
The SCO’s significance for India lies in economics and geopolitics with the Eurasian states.
- SCO is a potential platform to advance India’s Connect Central Asia policy. The SCO member states occupy the huge landmass adjacent to India’s extended neighbourhood where India has both economic and security imperatives.
- Importance of SCO-Afghanistan Contact Group to stabilise Afghanistan. SCO membership provides India a vital counter to some of the other groupings it is a part of.
- The SCO provides the only multilateral platform for India to deal in close proximity with Pakistan and Afghanistan.