CURRENT AFFAIRS
Get the most updated and recent current affair content on Padhaikaro.com
The Conference on Disarmament (CD)- Geneva
- IAS NEXT, Lucknow
- 06, Oct 2021
The Conference on Disarmament (CD) is being held in Geneva.
At the conference, India expressed deep concern over the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction and their delivery systems that could endanger peace and security, saying the
possibility of terrorists acquiring such weapons necessitates the global community to work together to address this grave danger.
- India has said that it supports the full and effective implementation of the Chemical Weapons Convention and emphasises the strengthening of the OPCW to fulfill its important mandate.
About the Conference on Disarmament:
The Conference on Disarmament (CD) is a multilateral disarmament forum established by the international community to negotiate arms control and disarmament agreements based at the Palais des Nations in Geneva. The Conference meets annually in three separate sessions in Geneva.
- The Conference was first established in 1979 as the Committee on Disarmament as the single multilateral disarmament negotiating forum of the international community. It was renamed the Conference on Disarmament in 1984.
- Formation: 1984.
- Membership: 65 Countries.
The Conference was created with a permanent agenda, also known as the “Decalogue,” which includes the following topics:
- Nuclear weapons in all aspects.
- Other weapons of mass destruction.
- Conventional weapons.
- Reduction of military budgets.
- Reduction of armed forces.
- Disarmament and development.
- Disarmament and international security.
Relationship to the United Nations:
The Conference is formally independent from the United Nations. However, while it is not formally a UN organization, it is linked to it in various ways.
- First and foremost, the Director-General of the United Nations Office at Geneva serves as the Secretary-General of the Conference.
- Furthermore, while the Conference adopts its own rules of procedure and agenda, the United Nations General Assembly can pass resolutions recommending specific topics to the Conference.
- Finally, the Conference submits a report of its activities to the General Assembly yearly, or more frequently, as appropriate.
About OPCW:
- It is an international organization established by the Chemical Weapons Convention, 1997 to implement and enforce the terms of the non-proliferation treaty, which prohibits the use, stockpiling, or transfer of chemical weapons by signatory states.
- The OPCW is authorized to perform inspections to verify that signatory states are complying with the convention.
- By the 2001 Relationship Agreement between the OPCW and the United Nations, the OPCW reports on its inspections and other activities to the UN through the office of the Secretary General.
- The organisation was awarded the 2013 Nobel Peace Prize “for its extensive efforts to eliminate chemical weapons”.
The Chemical Weapons Convention prohibits:
- Developing, producing, acquiring, stockpiling, or retaining chemical weapons.
- The direct or indirect transfer of chemical weapons.
- Chemical weapons use or military preparation for use.
- Assisting, encouraging, or inducing other states to engage in CWC-prohibited activity.
- The use of riot control agents “as a method of warfare.”
External auditor for Hague-based OPCW:
In April 2021, India’s Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) has been chosen as the external auditor by the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) for a three-year term starting 2021.
- The appointment was made through an election process at the OPCW conference recently.
- India was also selected as the member of the executive council of the OPCW representing Asia group for another two-year term during the OPCW conference.
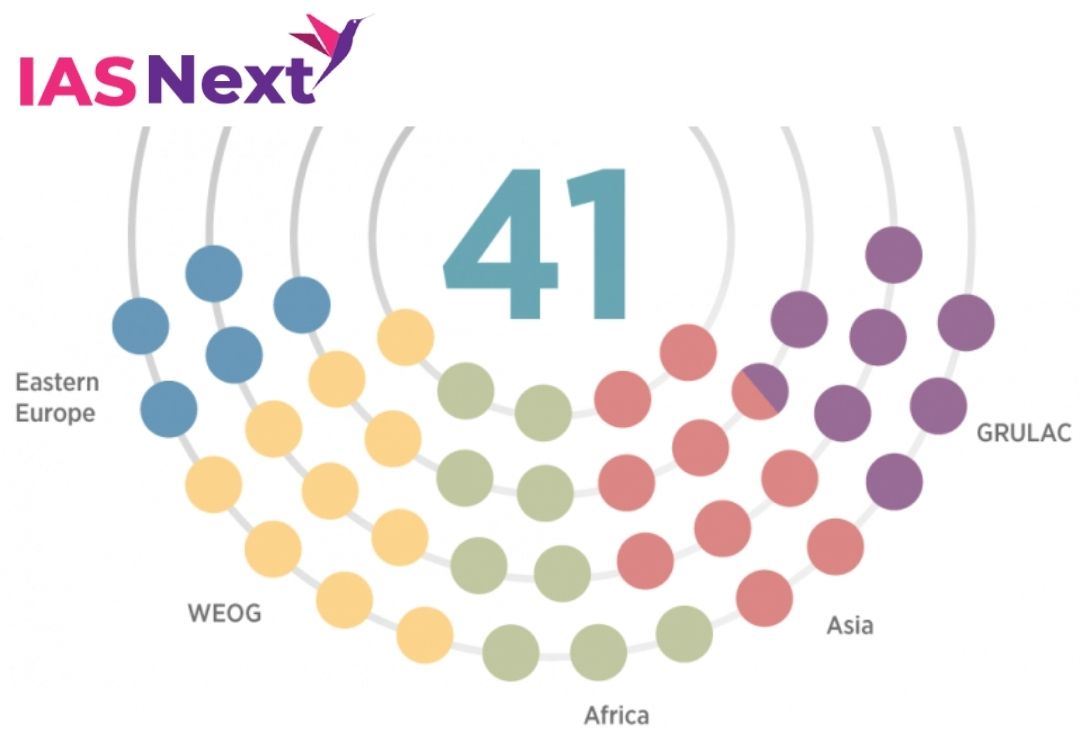
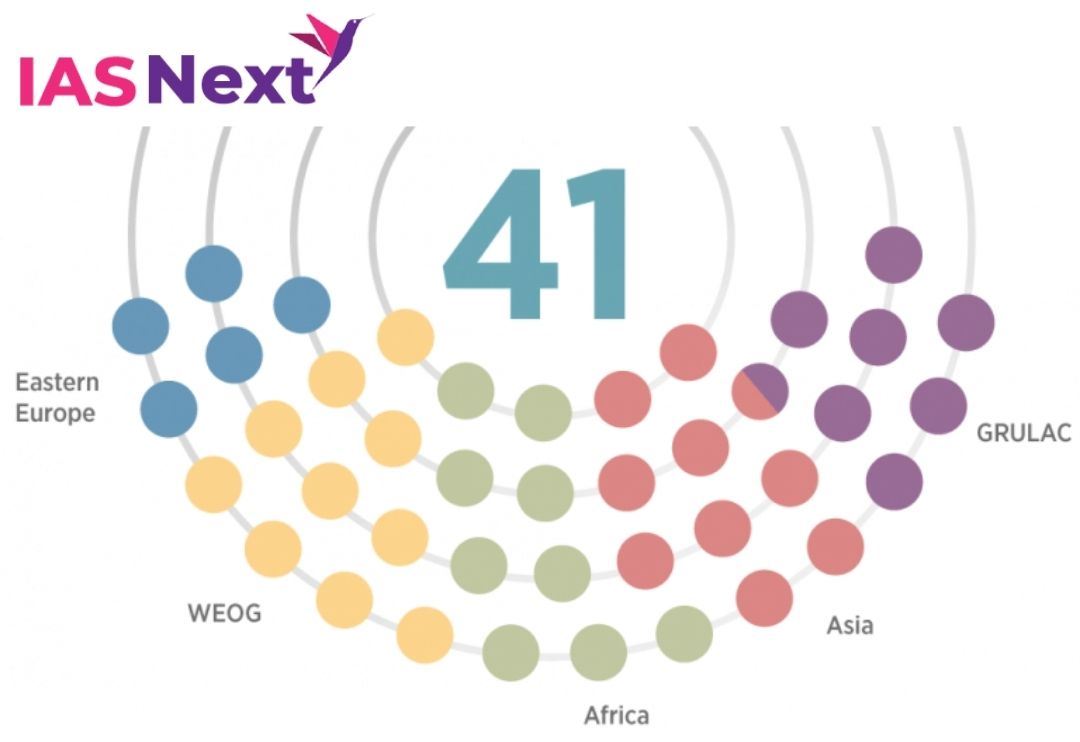
About the Executive Council:
- It is the governing body of the OPCW.
- The Council consists of 41 OPCW Member States that are elected by the Conference of the States Parties and rotate every two years.
- The Council supervises the activities of the Technical Secretariat and is responsible for promoting the effective implementation of and compliance with the Convention.
- Each Member State has the right, on a rotating basis, to serve on the Executive Council.