CURRENT AFFAIRS
Get the most updated and recent current affair content on Padhaikaro.com
The Future of Fly Ash in Concrete
- IAS NEXT, Lucknow
- 23, Nov 2021

Activists and fishermen have complained about fly ash making its way into the Kosasthalaiyar from the North Chennai Thermal Power Station (NCTPS). This was due to a leak in the pipeline carrying ash to the ash pond.
What is Fly Ash?
Popularly known as Flue ash or pulverised fuel ash, it is a coal combustion product.
Composition:
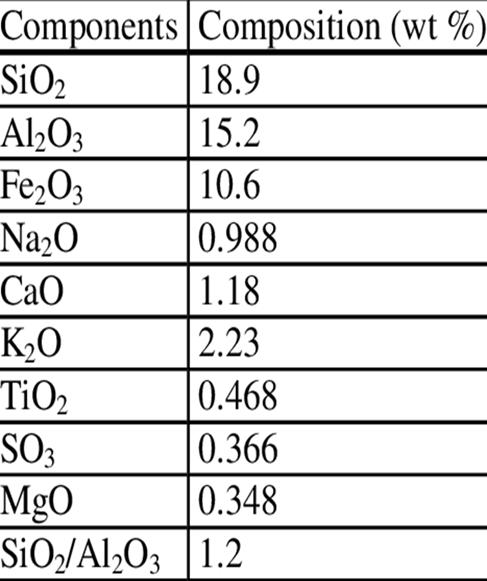
Composed of the particulates that are driven out of coal-fired boilers together with the flue gases.
- Depending upon the source and composition of the coal being burned, the components of fly ash vary considerably, but all fly ash includes substantial amounts of silicon dioxide (SiO2), aluminium oxide (Al2O3) and calcium oxide (CaO), the main mineral compounds in coal-bearing rock strata.
- Minor constituents include: arsenic, beryllium, boron, cadmium, chromium, hexavalent chromium, cobalt, lead, manganese, mercury, molybdenum, selenium, strontium, thallium, and vanadium, along with very small concentrations of dioxins and PAH compounds. It also has unburnt carbon.
Health and environmental hazards:
Toxic heavy metals present: All the heavy metals found in fly ash nickel, cadmium, arsenic, chromium, lead, etc—are toxic in nature. They are minute, poisonous particles accumulate in the respiratory tract, and cause gradual poisoning.
Radiation: For an equal amount of electricity generated, fly ash contains a hundred times more radiation than nuclear waste secured via dry cask or water storage.
Water pollution: The breaching of ash dykes and consequent ash spills occur frequently in India, polluting a large number of water bodies.
Effects on environment: The destruction of mangroves, drastic reduction in crop yields, and the pollution of groundwater in the Rann of Kutch from the ash sludge of adjoining Coal power plants has been well documented.
However, fly ash can be used in the following ways:
- Concrete production, as a substitute material for Portland cement, sand.
- Fly-ash pellets which can replace normal aggregate in concrete mixture.
- Embankments and other structural fills.
- Cement clinker production – (as a substitute material for clay).
- Stabilization of soft soils.
- Road subbase construction.
- As aggregate substitute material (e.g. for brick production).
- Agricultural uses: soil amendment, fertilizer, cattle feeders, soil stabilization in stock feed yards, and agricultural stakes.
- Loose application on rivers to melt ice.
- Loose application on roads and parking lots for ice control.